Andrew J. Pounds, Ph.D
Departments of Chemistry and Computer Science
Mercer University
The assumption is that you have some data from your laboratory that you need to graph and that the datafrom your experiment needs to be fit to a best fit line. This is easily accomplished in Excel.Let us assume that you have recorded the average number of bananas consumed per hour for various sizedcages of monkeys. In the diagram below I have entered the data.
I then need to highlight the data with the mouse.
The closer to 1.0, the better the fit of the regression line. That is, the closer the line passes through all of the points. Now lets look at another set of data done for this lab (Figure 7). Notice that the equation for the regression line is different than is was in Figure 6. I have investigated linest logest trend and forecast but these seem to deal with straight lines of best fit. Is there a way to generate coefficients for a polynomial best fit curve without making a best fit line and copying the values into different cells from the graph. Basic video on how to fit a linear line to data using something like a least squares method1) Trial and error method2) Least Squares3) Solver40 Using the 'Ad.
- You can fit text for multiple columns at once (as we will see later in examples) Autofit Row Height: This feature automatically adjusts the row height to fit the text in the cell. You can autofit multiple rows at once. In most cases, you would notice that Excel automatically adjusts the row height when you enter more than one line in the same cell.
- Excel has four ways to find the equation of a line: LINEST (or LOGEST) function, trendline on a chart, regression analysis in the DataAnalysis ToolPak, and Solver.
After I have the data selected I go to the top menu and hit the 'Insert' menu and select the 'Chart' submenu. Oncethe chart menu comes up, select the 'XY Scatter' chart type. The screen shouldthen look like what is seen below.
Hit the NEXT button and you will get the screen below.
At this point Excel is going to let me customize my plot by adding a title and axis labels. You should do this at a minimum. Other customizations are also possible but will not be discussed here. I have entered a title and axis labels for the data collected.
After hitting NEXT, I am taken to a screen that asks where the new chart is to be drawn. Select 'As new sheet' as shown in the figure below.
Once I have gotten to this point I can hit FINISH. Excel will then draw the chart in a new sheet in the current workbook and placeme on that sheet. It will look something like the screen shot below.
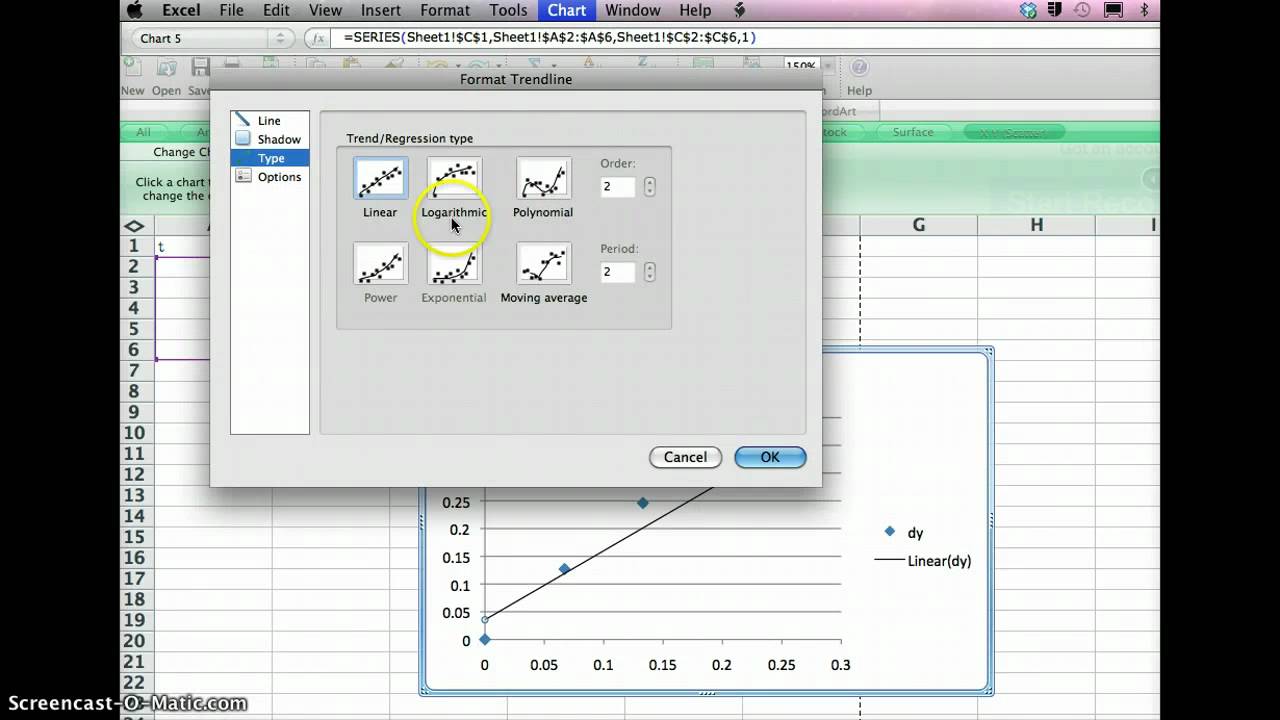
Now the task is to add the best fit line. Excel calls this a trendline. To start this process select the 'Chart' menu option and the 'Add Trendline' menu suboption. You will be presented with a selection box that looks like the following. Select the 'Linear' regression type as indicated.
Then select the 'Options' tab.Add any custom title you want for the best fit line, and check the box to Display the equation on the chartas indicated below.
Once you have done this, select 'OK' and the chart, with the associated best fit line should appear on your chart along with the equation for the best fit line.

The Excel Logest Function calculates the exponential curve that best fits a supplied set of y- and x- values.
Best Fit Line Excel 2016
If there is a single range of x-values, the calculated exponential curve satisfies the equation:
where,
- x is the independent variable;
- y is the dependent variable;
- m is a constant base for the x value;
- b is a constant which is the value of y when x = 0.
If there are multiple ranges of x-values, the calculated exponential curve satisfies the following equation:
where,- the x's are the independent variable ranges;
- y is the dependent variable;
- the m's are constant bases for the x values;
- b is a constant.
Function Description
The Excel LOGEST function returns statistical information on the exponential curve of best fit, through a supplied set of x- and y- values.
The basic statistical information returned is the array of constants, mn, mn-1, ... , b (or the constants m and b if there is a single range of x-values), for the exponential curve equation. However, you can also request that additional regression statistics be returned.
The syntax of the Logest function is:
where the function arguments are as follows:
| known_y's | - | An array known y-values. | ||||||
| [known_x's] | - | An optional argument, providing an array of one or more sets of known x-values. If provided the [known_x's] array should have the same length as the known_y's array; If omitted, the [known_x's] array takes on the default value {1, 2, 3, ...}). | ||||||
| [const] | - | An optional logical argument that determines how the constant 'b' is treated in the exponential curve equation y = b*m^x. This argument can have the value TRUE or FALSE, meaning: | ||||||
| ||||||||
| [stats] | - | An optional logical argument which specifies whether or not you want the function to return additional regression statistics on the calculated curve. This argument can have the value TRUE or FALSE, meaning: | ||||||
| ||||||||
The array of statistics returned from the Excel Logest function has the following form:
| mn | mn-1 | ... | m1 | b |
| sen | sen-1 | ... | se1 | seb |
| r2 | sey | |||
| F | df | |||
| ssreg | ssresid |
where the statistics returned are:
| mi | - | The array of constant base coefficients for the exponential curve equation |
| b | - | The constant value of y when x=0 |
| sei | - | The standard error values for the coefficients, mi |
| seb | - | the standard error value for the constant b (returns the #N/A error if the [const] argument is FALSE) |
| r2 | - | The coefficient of determination |
| sey | - | The standard error for the y estimate |
| F | - | The F statistic, or the F-observed value |
| df | - | The number of degrees of freedom |
| ssreg | - | The regression sum of squares |
| ssresid | - | The residual sum of squares |
To input an array formula, you need to first highlight the range of cells for the function result. Type your function into the first cell of the range, and press CTRL-SHIFT-Enter.
Go to the Excel array formulas page for more details.As the Logest function returns an array of values, it must be entered as an array formula. If the function is not entered as an array formula, only the first 'm' value in the calculated array of statistical information is returned.
You can see if a function has been input as an array formula, as curly brackets will be inserted around the formula, as it is viewed in the formula bar. This can be seen in the examples below.
Best Fit Line Excel
Logest Function Example 1
Cells A2-A10 and B2-B10 of the spreadsheet below list a number of known x and known y values, and also shows these points, plotted on a chart. Cells D1-E5 of the spreadsheet show the results of the Excel Logest function, which has been used to return statistical information relating to the exponential curve of best fit through these points.
As shown in the formula bar, the formula for the Logest function is:
The curly brackets around this function show that it has been entered as an array formula.
Cells D1 and E1 give the values of the base, m as 1.482939831, and the y-intercept, b as 2.257475168. Therefore, the equation for the exponential curve of best fit through the given points is:
The remaining cells in the range D1-E5 give the following additional statistics for this curve:
- The standard error value for the base m is 0.014718308
- The standard error value for the constant b is 0.070073164
- The coefficient of determination is 0.990327432
- The standard error for the y estimate is 0.114007527
- The F statistic is 716.6960934
- The number of degrees of freedom is 7
- The regression sum of squares is 9.315412472
- The residual sum of squares is 0.090984014
Logest Function Example 2
Cells A2-A11, B2-B11 and C2-C11 of the spreadsheet below contain three different sets of independent variables (known x values), and cells D2-D11 of the spreadsheet contain the associated known y-values. Cells F1-H3 of the spreadsheet show the results of the Excel Logest function, which has been used to return statistical information relating to the exponential curve of best fit through these points.
As shown in the formula bar, the formula for the Logest function in this case is:
It is also seen, from the surrounding curly brackets, that the function has been entered as an array formula.
Cells F1-I1 give the values of the coefficents, m3, m2 and m1 as 2.010750937, 0.942167056 and 1.31373656, respectively and the y-intercept, b as 2.554652779. Therefore, the equation for the exponential curve of best fit through the given points is:
Best Fit Line Excel 2013
The remaining cells in the range F1-I5 give the following additional statistics for this curve:
- The standard error values for the coefficients m3, m2 and m1are 0.080315977, 0.012928031 and 0.04764347, respectively
- The standard error value for the constant b is 0.275195565
- The coefficient of determination is 0.997749047
- The standard error for the y estimate is 0.057701675
- The F statistic is 886.5125548
- The number of degrees of freedom is 6
- The regression sum of squares is 8.854886129
- The residual sum of squares is 0.0199769
and the unused cells show the #N/A error.
For further information and examples of the Excel Logest function, see the Microsoft Office website.
Logest Function Errors
If you get an error from the Excel Logest function this is likely to be one of the following:
| #REF! | - | Occurs if the array of [known_x's] is not the same length as the array of known_y's. |
| #VALUE! | - | Occurs if either:
|
Return to the List of All Built-In Excel Functions